Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- c3 step graph
- InfluxDB
- c++ 정규식
- python subprocess
- c3 second
- gcc regex
- grafana dashboard
- 정규식 활용
- 백준
- c3 초
- 정규식 문자열 출력
- snmp
- c3 축 가리기
- c3 축 없애기
- snmp test
- python os
- python popen
- selinux port 등록
- centos pyhon 설치
- telegraf
- linux시간으로 변경
- 정규식 컴파일
- g++ 업데이트
- influxdb 설치
- subporcess path
- 1697
- regex_search
- CentOS7
- semanage
- gcc 업데이트
Archives
- Today
- Total
리셋 되지 말자
캡슐화: 정보 은닉 본문
접근 제어자
- 자바에서 정보 은닉(information hiding)이라고 하면 접근 제어자인 private, [default], protected, public이 생각난다. 이 외에 접근자 및 설정자 메서드도 생각이 날 수 있다.
- 접근 제어자가 객체 멤버(인스턴스 멤버)와 쓰일 때와 정적 멤버(클래스 멤버)와 함께 쓰일때를 비교해본다.
객체 멤버의 접근 제어자
- 아래와 같이 패키지와 클래스가 있다고 가정하자
- 자신의 멤버가 아닌 다른 객체의 멤버에 접근하는 경우에는 다른 객체를 생성한 후 접근해야 한다.
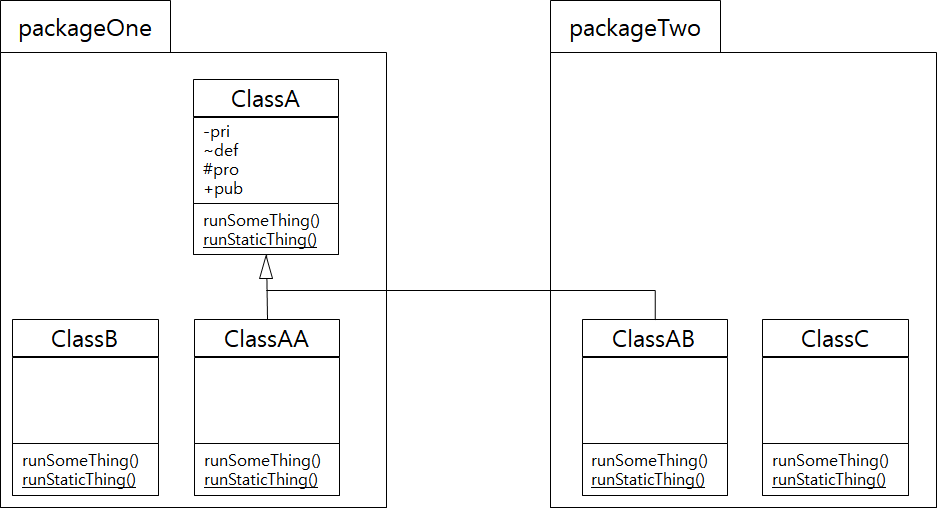
- UML 표기법에서 - 표시는 private 접근 제어자, ~ 표시는 [default], # 표시는 protected, + 표시는 public 접근 제어자를 나타낸다.
- 속성이나 메서드 아래에 _(밑줄)을 사용한 경우는 정적 멤버를 나타낸다.
- ClassA를 java 코드로 구현하면 아래와 같다
package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassA {
private int pri;
int def;
protected int pro;
public int pub;
void runSomething() {
}
static void runStaticThing() {
}
}- 각 패키지의 함수에서 접근할 수 있는 ClassA의 속성은 다음과 같다.
|
ClassA의 객체 멤버 |
||||||
|
pri |
def |
pro |
pub |
|||
|
PackageOne |
ClassA |
runSomeThing() |
||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassB |
runSomething() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassAA |
runSomeThing() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
PackageTwo |
ClassAB |
runSomeThing() |
||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassC |
runSomeThing() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
각 클래스에서 main 함수로 접근
- ClassA 에서의 접근
package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassA {
private String pri="private";
String def = "default";
protected String pro = "protected";
public String pub = "public";
void runSomething() {
System.out.print("rung something\n");
}
static void runStaticThing() {
System.out.print("rung static thing\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
System.out.println(classA.pri);
System.out.println(classA.def);
System.out.println(classA.pro);
System.out.println(classA.pub);
classA.runSomething();
classA.runStaticThing();
}
}
- ClassB 에서의 접근
package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
//System.out.println(classA.pri); 오류 발생
System.out.println(classA.def);
System.out.println(classA.pro);
System.out.println(classA.pub);
classA.runSomething();
classA.runStaticThing();
}
}
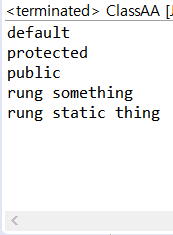
- ClassAA 에서의 접근
package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassAA extends ClassA{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
// System.out.println(classA.pri);
System.out.println(classA.def);
System.out.println(classA.pro);
System.out.println(classA.pub);
classA.runSomething();
classA.runStaticThing();
}
}
- ClassAB 에서의 접근
package encapsulation01.packageTwo;
import encapsulation01.packageOne.ClassA;
public class ClassAB extends ClassA{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
//System.out.println(classA.pri);
//System.out.println(classA.def);
//System.out.println(classA.pro);
System.out.println(classA.pub);
//classA.runSomething();
//classA.runStaticThing();
}
}
- ClassC 에서의 접근
package encapsulation01.packageTwo;
import encapsulation01.packageOne.ClassA;
public class ClassC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassA classA = new ClassA();
// System.out.println(classA.pri);
// System.out.println(classA.def);
// System.out.println(classA.pro);
System.out.println(classA.pub);
// classA.runSomething();
// classA.runStaticThing();
}
}
이번엔 정적 속성일 때이다.
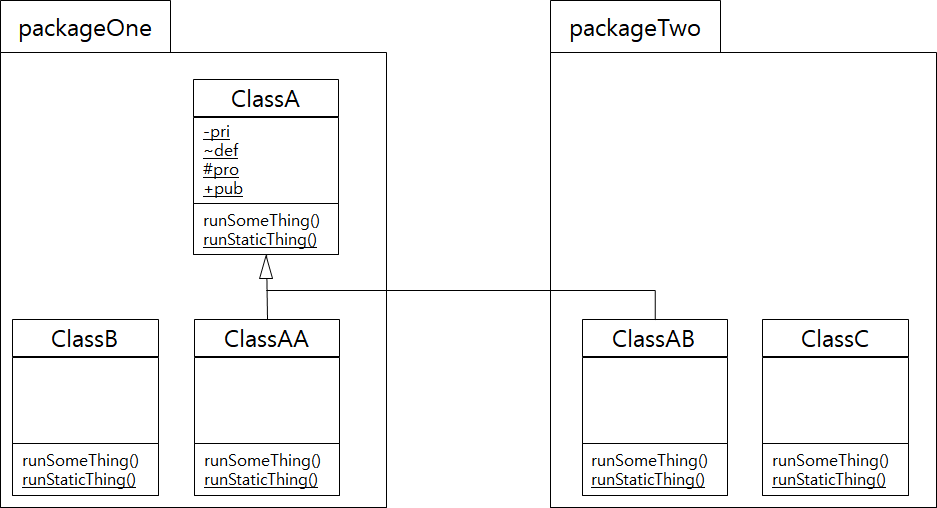
- 각 패키지의 함수에서 접근할 수 있는 ClassA의 속성은 다음과 같다.
|
ClassA의 정적 멤버 |
||||||
|
pri |
def |
pro |
pub |
|||
|
PackageOne |
ClassA |
runSomeThing() |
||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassB |
runSomething() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassAA |
runSomeThing() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
PackageTwo |
ClassAB |
runSomeThing() |
||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
|
ClassC |
runSomeThing() |
|||||
|
runStaticThing() |
||||||
교재 제공 소스
package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassA {
private int pri;
int def;
protected int pro;
public int pub;
static private int priStatic;
static int defStatic;
static protected int proStatic;
static public int pubStatic;
void runSomething() {
pri = 1;
this.pri = 1;
def = 1;
this.def = 1;
pro = 1;
this.pro = 1;
pub = 1;
this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
ClassA.priStatic = 1;
priStatic = 1;
this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1;
defStatic = 1;
this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1;
proStatic = 1;
this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1;
pubStatic = 1;
this.pubStatic = 1;
}
static void runStaticThing() {
// 객체를 생성하지 않고는 객체 멤버 접근 불가
// pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
// def = 1; this.def = 1;
// pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
// pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
ClassA.priStatic = 1;
priStatic = 1; // this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1;
defStatic = 1; // this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1;
proStatic = 1; // this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1;
pubStatic = 1; // this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassA ca = new ClassA();
ca.pri = 1;
ca.def = 1;
ca.pro = 1;
ca.pub = 1;
// 객체 참조 변수를 통해 정적 멤버도 접근 가능, 권장하지는 않음
ca.priStatic = 1;
ca.defStatic = 1;
ca.proStatic = 1;
ca.pubStatic = 1;
}
}package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassAA extends ClassA {
void runSomething() {
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
def = 1; this.def = 1;
pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; priStatic = 1; this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1; defStatic = 1; this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; proStatic = 1; this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; pubStatic = 1; this.pubStatic = 1;
}
static void runStaticThing() {
// 객체를 생성하지 않고는 객체 멤버 접근 불가
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; priStatic = 1; //this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1; defStatic = 1; //this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; proStatic = 1; //this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; pubStatic = 1; //this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassAA caa = new ClassAA();
//ca.pri = 1;
caa.def = 1;
caa.pro = 1;
caa.pub = 1;
// 객체 참조 변수를 통해 정적 멤버도 접근 가능, 권장하지는 않음
//ca.priStatic = 1;
caa.defStatic = 1;
caa.proStatic = 1;
caa.pubStatic = 1;
}
}package encapsulation01.packageOne;
public class ClassB {
void runSomething() {
// 상속을 받지 않았기에 ClassA 의 객체 멤버는 객체 생성 후에 접근 가능
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; //priStatic = 1; this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1; //defStatic = 1; this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; //proStatic = 1; this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; //pubStatic = 1; this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassA ca = new ClassA();
//ca.pri = 1;
ca.def = 1;
ca.pro = 1;
ca.pub = 1;
}
static void runStaticThing() {
// 객체를 생성하지 않고는 객체 멤버 접근 불가
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; //priStatic = 1; //this.priStatic = 1;
ClassA.defStatic = 1; //defStatic = 1; //this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; //proStatic = 1; //this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; //pubStatic = 1; //this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassA ca = new ClassA();
//ca.pri = 1;
ca.def = 1;
ca.pro = 1;
ca.pub = 1;
// 객체 참조 변수를 통해 정적 멤버도 접근 가능, 권장하지는 않음
//ca.priStatic = 1;
ca.defStatic = 1;
ca.proStatic = 1;
ca.pubStatic = 1;
}
}package encapsulation01.packageTwo;
import encapsulation01.packageOne.ClassA;
public class ClassAB extends ClassA {
void runSomething() {
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; priStatic = 1; this.priStatic = 1;
//ClassA.defStatic = 1; defStatic = 1; this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; proStatic = 1; this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; pubStatic = 1; this.pubStatic = 1;
}
static void runStaticThing() {
// 객체를 생성하지 않고는 객체 멤버 접근 불가
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; priStatic = 1; //this.priStatic = 1;
//ClassA.defStatic = 1; defStatic = 1; //this.defStatic = 1;
ClassA.proStatic = 1; proStatic = 1; //this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; pubStatic = 1; //this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassAB cab = new ClassAB();
//ca.pri = 1;
//ca.def = 1;
cab.pro = 1;
cab.pub = 1;
// 객체 참조 변수를 통해 정적 멤버도 접근 가능, 권장하지는 않음
//ca.priStatic = 1;
//cab.defStatic = 1;
cab.proStatic = 1;
cab.pubStatic = 1;
}
}package encapsulation01.packageTwo;
import encapsulation01.packageOne.ClassA;
public class ClassC {
void runSomething() {
// 상속을 받지 않았기에 ClassA 의 객체 멤버는 객체 생성 후에 접근 가능
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; //priStatic = 1; this.priStatic = 1;
//ClassA.defStatic = 1; //defStatic = 1; this.defStatic = 1;
//ClassA.proStatic = 1; //proStatic = 1; this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; //pubStatic = 1; this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassA ca = new ClassA();
//ca.pri = 1;
//ca.def = 1;
//ca.pro = 1;
ca.pub = 1;
}
static void runStaticThing() {
// 객체를 생성하지 않고는 객체 멤버 접근 불가
//pri = 1; this.pri = 1;
//def = 1; this.def = 1;
//pro = 1; this.pro = 1;
//pub = 1; this.pub = 1;
// 정적 멤버는 클래스명.정적멤버 형태의 접근을 권장
//ClassA.priStatic = 1; //priStatic = 1; //this.priStatic = 1;
//ClassA.defStatic = 1; //defStatic = 1; //this.defStatic = 1;
//ClassA.proStatic = 1; //proStatic = 1; //this.proStatic = 1;
ClassA.pubStatic = 1; //pubStatic = 1; //this.pubStatic = 1;
// 객체 멤버를 객체 생성 후에 객체 참조 변수를 통해 접근 가능
ClassA ca = new ClassA();
//ca.pri = 1;
//ca.def = 1;
//ca.pro = 1;
ca.pub = 1;
// 객체 참조 변수를 통해 정적 멤버도 접근 가능, 권장하지는 않음
//ca.priStatic = 1;
//ca.defStatic = 1;
//ca.proStatic = 1;
ca.pubStatic = 1;
}
}
Comments
